Treatment of Upper Esophageal Dysphagia (Z-POEM)
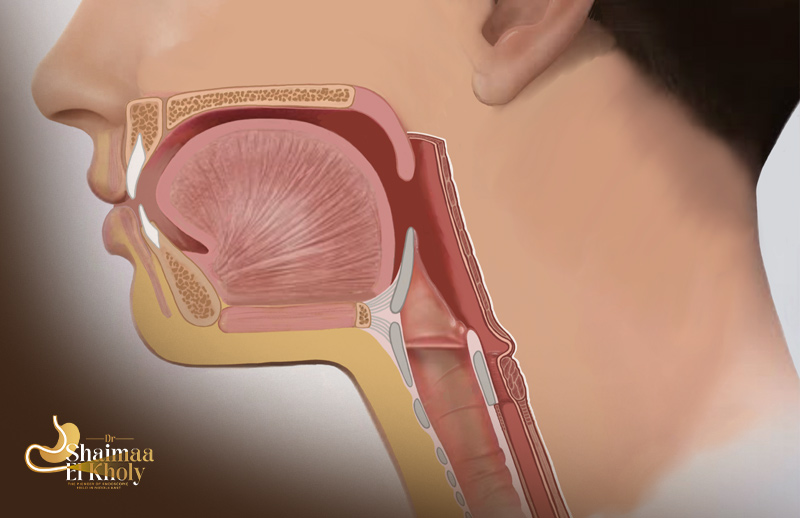
The diverticulum refers to an abnormal pouch that forms outside the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. Zenker’s diverticulum, or pharyngoesophageal diverticulum, is a rare disorder characterized by the formation of a pharyngeal pouch just above the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), where the lower part of the throat meets the upper esophagus. This pouch develops when the muscles below it become overly tense, preventing food from entering the esophagus, and ultimately leading to difficulty swallowing. It commonly occurs in males and older adults.
Causes of pharyngoesophageal diverticulum:
Reports indicate an incidence rate of 2 per 100,000 annually, but the exact causes remain unknown. Zenker’s diverticulum develops when the muscle between the throat and esophagus, known as the upper esophageal sphincter or pharyngoesophageal muscle, becomes tense.
As this muscle tightens, pressure builds along the throat wall above the sphincter. There is a relative weakness in the wall of the throat just above this muscle, and the pouch forms due to the increased relative pressure exerted on this weak area during swallowing. Over time, the pouch can enlarge due to excessive tension in the underlying muscles.
Because the upper esophageal sphincter underneath the pouch is tighter than normal, it becomes difficult for food and liquids to pass into the esophagus, often causing them to divert into the pouch or even back into the throat. This condition can also complicate the swallowing of medications, especially pills. Consequently, treatment methods have focused on performing a pharyngeal myotomy. The latest technique for this procedure is the third-space endoscopy, which relies on endoscopic methods and is performed non-surgically through the Z-POEM technique with Dr. Shaimaa El Kholy, Associate Professor of Advanced Interventional Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESD & Third Space Endoscopy), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University.
Symptoms of pharyngoesophageal diverticulum:
A person with Zenker's diverticulum may experience the following symptoms:
• Difficulty swallowing.
• A sensation of food sticking in the throat.
• Bad breath.
• Chronic cough.
• The feeling of excess mucus in the throat.
• The sensation of a lump in the throat.
• Regurgitation of food back into the mouth (often several hours after eating).
• Weight loss due to difficulty eating and consequent malnutrition.
• Choking.
• Accumulation of swallowed substances in the pouch leads to vomiting long after a meal.
• Difficulty swallowing pills.
Some individuals with Zenker's diverticulum may only experience mild symptoms, but over time, the pouch grows, and symptoms become more pronounced.
Diagnosis of pharyngoesophageal diverticulum:
• Upper gastrointestinal barium contrast radiography:
An upper gastrointestinal barium contrast radiography is performed to assess swallowing efficiency. It shows how well a person can move liquid or food from the mouth to the throat and the esophagus. The patient swallows food mixed with barium, which is visible on X-ray. This study evaluates whether swallowing occurs abnormally.
• Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is a procedure used to visualize the upper part of the esophagus and surrounding structures. It involves a long, flexible tube with a small light and video camera at the end. The endoscope is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus to assess symptoms and signs of esophageal disease. Several esophageal abnormalities can be diagnosed through this upper endoscopy. This diagnostic endoscopy is an outpatient procedure. It takes less than 5 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia.
Sometimes, Zenker's diverticulum is diagnosed incidentally during tests performed for other reasons.
Treatment of pharyngoesophageal diverticulum:
The goal of treating Zenker's diverticulum is to alleviate swallowing obstruction caused by narrowing above the esophageal sphincter, facilitate the passage of swallowed materials, and eliminate their accumulation in the diverticulum.
Previous methods for treating Zenker's diverticulum:
For patients with mild cases, changing dietary habits, such as drinking water after meals or thoroughly chewing food, may be effective.
Also, some medications, such as Botox, have provided temporary relief for Zenker's diverticulum cases that are less than 1 cm or for patients who are not candidates for surgery.
Before the Z-POEM procedure, two surgical options were available:
• Laser or stapler usage: These methods often led to a loosening of the staples over time, resulting in pouch reformation.
• Surgical intervention: This was the primary treatment for many years, despite relatively high rates of complications and side effects, making it less safe for many elderly patients. This intervention involved a surgical cut in the neck to cut the muscle and possibly remove the diverticular pouch to allow food to pass during swallowing.
Later, various laparoscopic treatments were introduced to reduce complication rates. Laparoscopic intervention aimed to cut the barrier but carried risks of perforation and incomplete cuts, leading to higher recurrence rates.
The latest method for treating Zenker's diverticulum with third-space endoscopy:
Patients with Zenker's diverticulum now have an effective and safe alternative through the third space endoscopy technique (Z-POEM), derived from the POEM technique for treating achalasia or swallowing difficulties.
In recent years, the treatment of Zenker's diverticulum has begun through endoscopic muscle incision (Z-POEM), which is based on the tunnel concept known as third space endoscopy. The application of POEM has recently expanded to address some esophageal issues endoscopically. After undergoing the Z-POEM procedure, food can easily enter the esophagus without getting trapped in Zenker's diverticulum.
Steps of Z-POEM:
1. Z-POEM is performed under general anesthesia using endoscopic techniques.
2. A specific solution is injected to separate the layers of the esophageal wall.
3. Dr. Shimaa El Kholy uses a small knife to make a small incision in the esophageal lining to create an entry point for the tunnel between the layers of the esophageal wall.
4. Once the septum is accessed, the tunnel is extended on both sides of the muscular septum, one side to the right of the upper esophageal sphincter and the other to the left.
5. After fully exposing the muscle, this muscle is cut to create a common space, allowing food to move easily into the esophagus.
6. Dr. Shaimaa then closes the tunnel opening with small clips about one centimeter. Once the opening heals, these clips will fall off and travel down the esophagus to the stomach, exiting via the stool.
7. Finally, Dr. Shaimaa withdraws the endoscope.
8. The procedure takes only half an hour, and patients can return home within 24 hours.
Due to the continuous desire to improve outcomes, Dr. Shimaa El Kholy and the medical team have modified the technique by adding a step to cut excess mucosa after cutting the muscular septum, as the presence of mucosa was causing some symptoms to persist in certain cases.
Features of Z-POEM:
• Z-POEM is an ingenious solution that successfully addresses the shortcomings of traditional surgical and laparoscopic interventions without surgery.
• It is more effective than conventional surgery and leads to fewer side effects.
• There is a long-term improvement in symptoms for over 90% of patients.
• It is an endoscopic procedure rather than a surgical one; this means there are no incisions in the neck or throat, making it less risky than surgery.
• Zenker's diverticulum typically occurs in elderly patients who have comorbid conditions that prevent them from undergoing open surgery.
• There is no risk of perforation.
• It is a very safe procedure, allowing for faster recovery.
• The recurrence rate is lower compared to surgical options (less than 10%) due to the availability of better and more detailed images of the septum and the ability to reach its end compared to traditional diverticulum resection.
Therefore, there is no need to resort to surgery or less efficient traditional methods. You can be treated with the latest global techniques using third space endoscopy in Egypt with Dr. Shimaa El Kholy, Associate Professor of Advanced Interventional Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESD & Third Space Endoscopy), Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, who has achieved outstanding results.
